Stair Traversal Exploration Platform
Date:
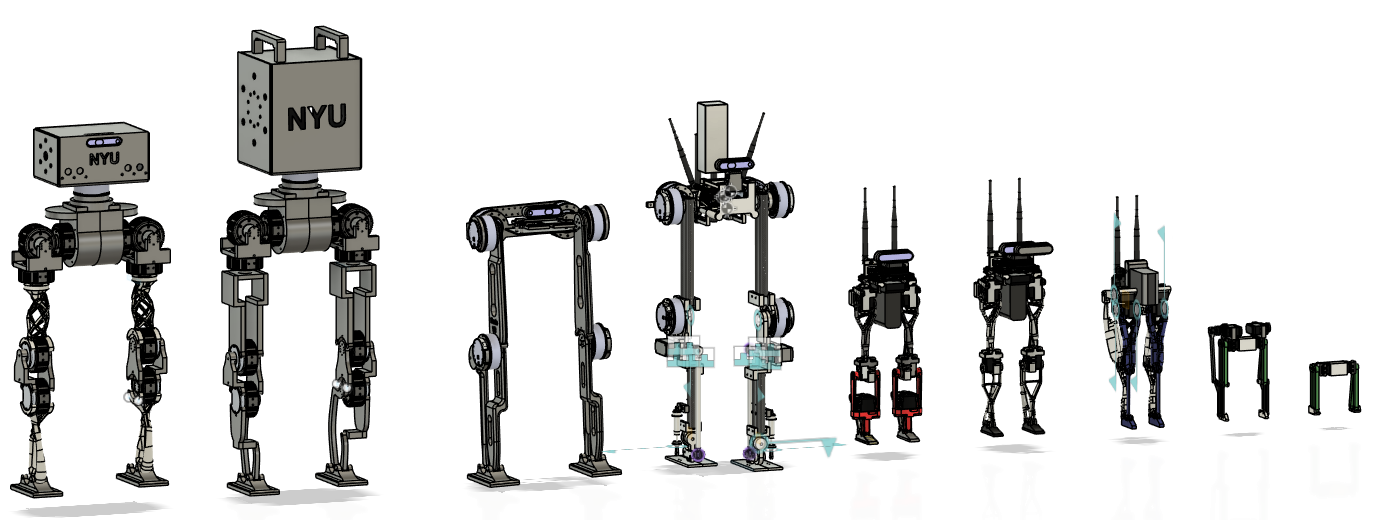

Project STEP began as a scrappy capstone project at NYU. We were a group of curious engineers trying to build humanoid robots that could walk. No frills, just a mission to make something move. Over time, it grew into a formal student team where both undergraduates and graduate students could contribute through a credit-bearing course or as volunteers.
As the inaugural team lead, I focused on the mechanical design and development of the next generation of bipeds, using insights from previous failures to create more modular, manufacturable systems. At the same time, I took on team operations, marketing, fundraising, budgeting, and mentoring a vertically integrated group of students from different academic levels.
I successfully secured sponsorships and raised funds, including a significant hardware grant from SendCutSend. This allowed us to move from 3D-printed prototypes to robust, CNC-machined and sheet metal designs, which elevated the quality and realism of our robots.
I personally designed, built, and tested multiple robots that combined carbon fiber, 3D printing, and machined components. I am now leading development on a 12-degree-of-freedom biped designed for easy fabrication, quick assembly, and future research adaptability.
I also introduced topology optimization and DFMA principles to improve performance and accelerate iteration. Today, STEP is not just a project but a living robotics platform that blends real-world engineering, collaboration, and student-led innovation.
Design Philosophy & Inspiration
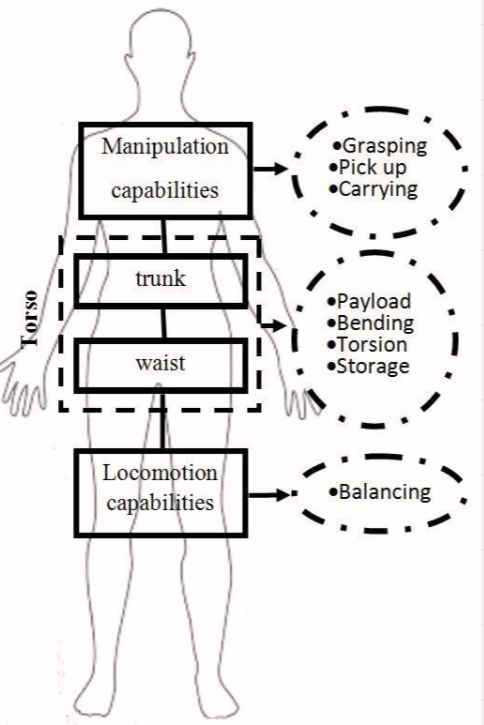
This image highlights the elegance and complexity of the human body. My goal was to design a biped that could realistically mimic human locomotion.
The core design philosophy behind STEP is grounded in bio-inspiration and iterative prototyping.
Early Development & Brainstorming

Team brainstorming board: design sketches and ideas
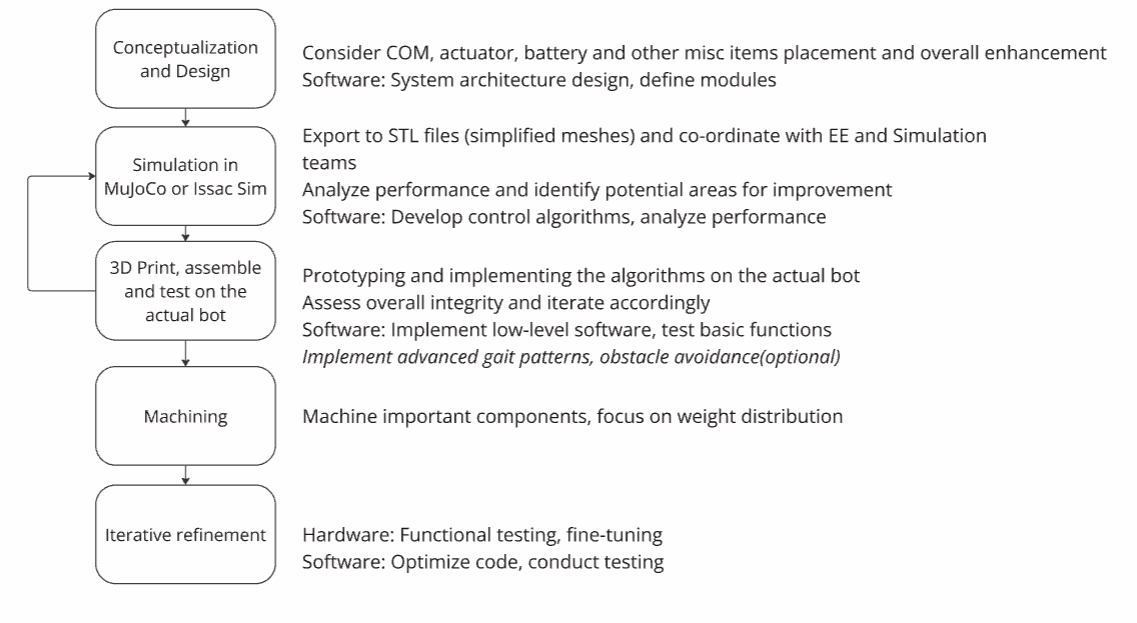
Development workflow: from CAD to prototype
Mechanical Development
13 DOF Robot Design
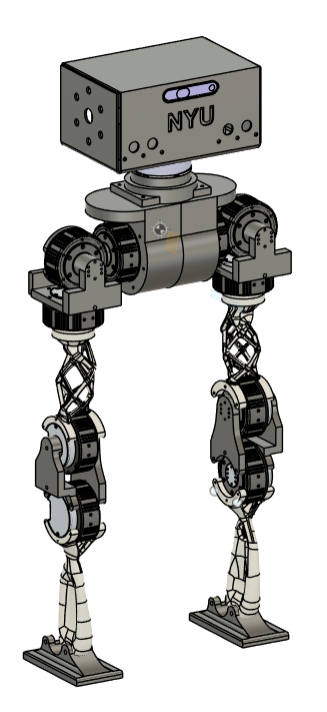
Isometric view
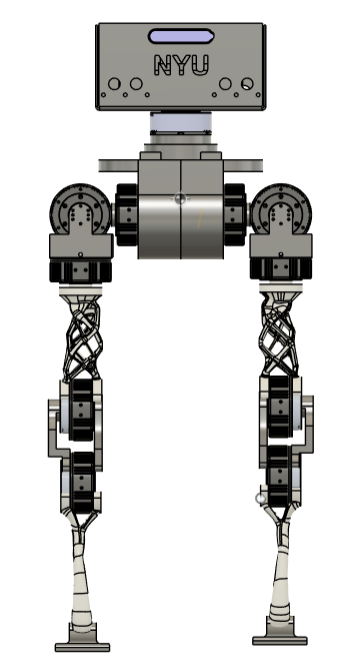
Front view
This bot was designed using a hybrid approach: sheet metal fabrication for structural components, CNC machining for precision parts, and 3D printing for rapid prototyping.
Generative Design for Weight Optimization
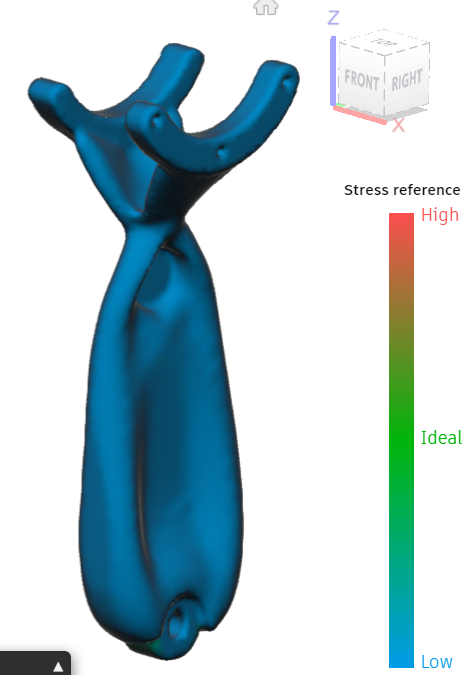
Generative design: Shin link
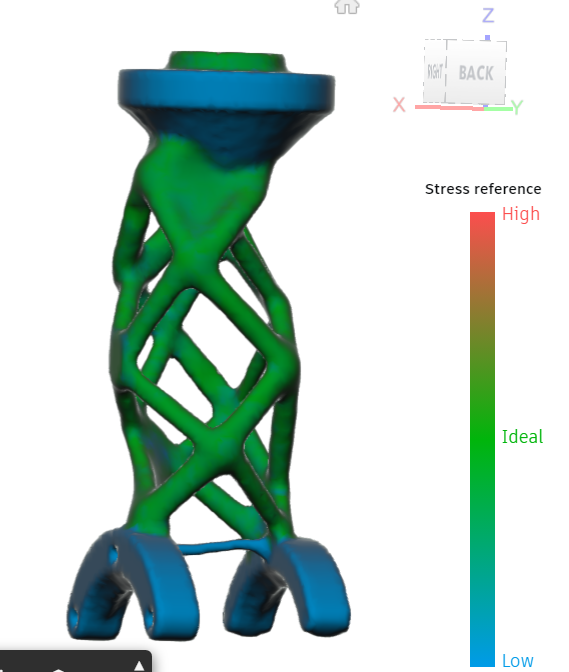
Generative design: Thigh link
CAD & Fabrication Prep
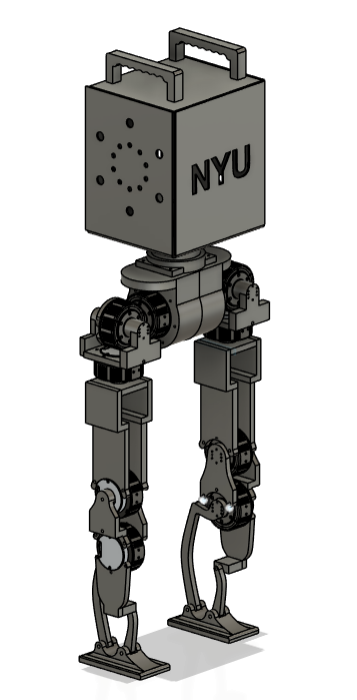
CAD model showing the 13 DOF robot prepared for fabrication.
Previous Versions
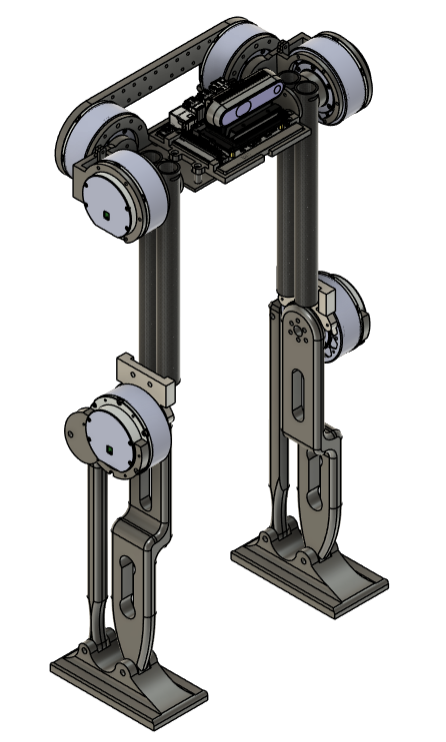

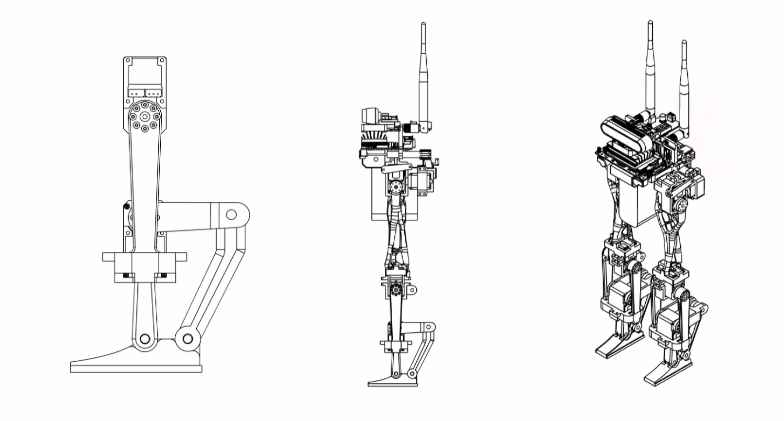
Control Development
Simulation of the 10 DOF bot walking using PPO (Proximal Policy Optimization). The URDF model was optimized specifically for sim-to-real transfer.
Public Showcase
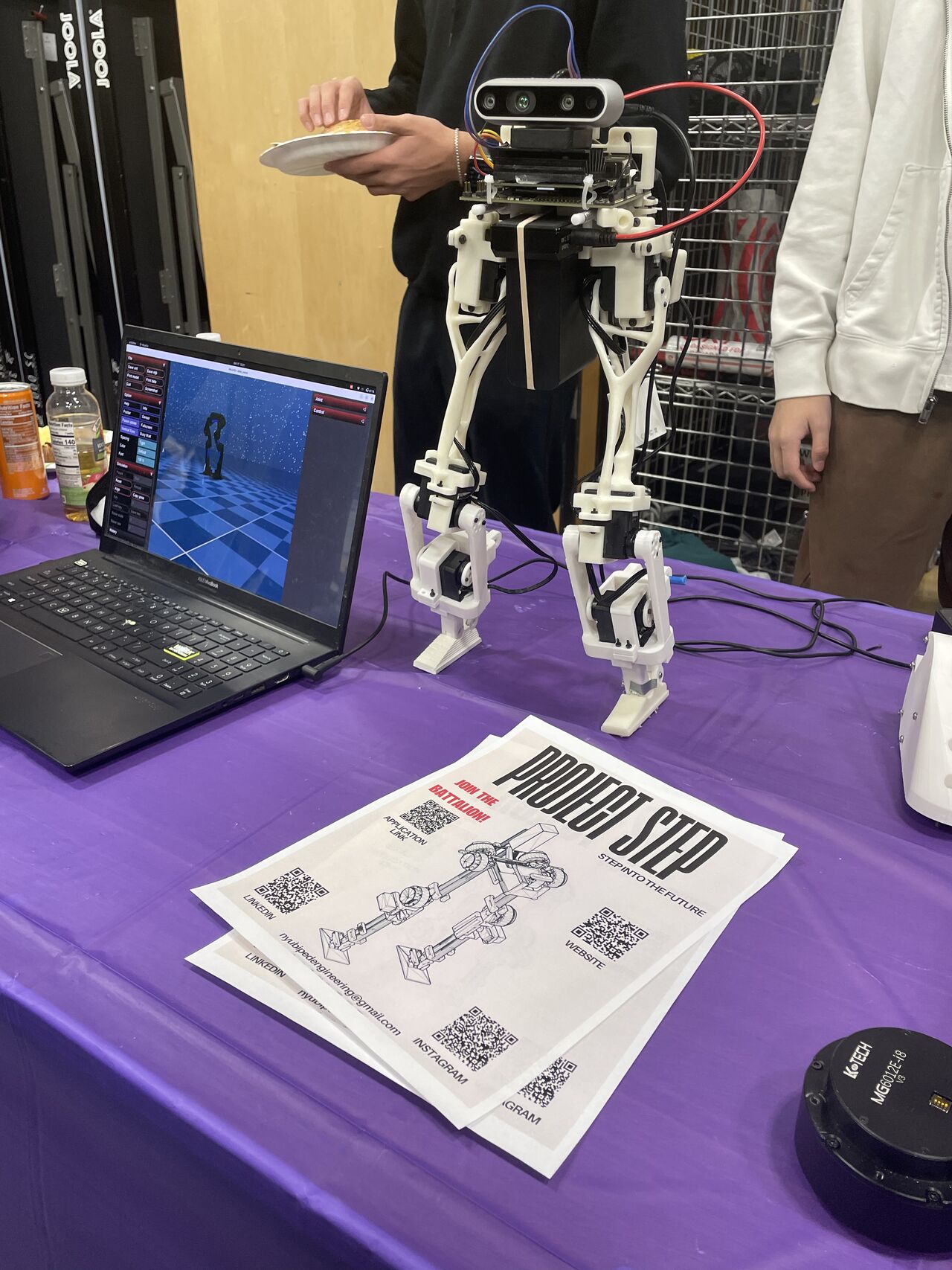

The robot showcased during an NYU event, highlighting both its design and control capabilities.
Current Status
Currently fabricating the latest generation of bipeds, including a finalized 13 DOF robot and an upgraded 12 DOF variant with modular joints and better ankle articulation. These are designed to be easily manufacturable, research-adaptable, and control-system ready.
This site is still a work in progress. Stay tuned for more updates as Project STEP continues to grow.
In the meantime, check out Project STEP for more!
