Maze Solving Device
Date:
Overview
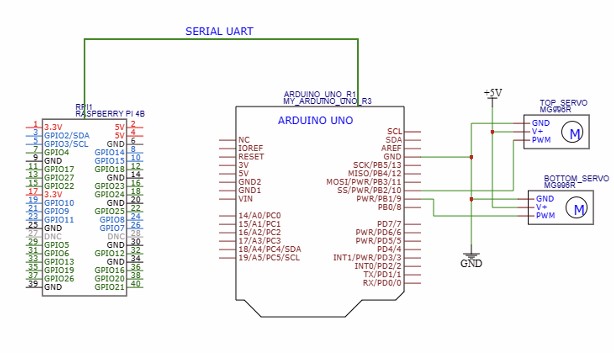
This project amalgamates the capabilities of Raspberry Pi 4B and Arduino Uno microcontrollers to create an innovative maze-solving robot.Utilizing OpenCV for image processing and implementing breadth-first search algorithms on the Raspberry Pi, the system intelligently navigates the ball towards the maze’s exit. By employing two servos controlled by the Arduino, the project orchestrates the movement of a ball through complex mazes
Objectives
1.Develop a reliable ball detection algorithm using OpenCV to accurately identify the position of the ball within maze and differentiating walls of maze from base.
- Implement preprocessing techniques to facilitate maze detection.
- Utilize contour detection to precisely locate the center of the ball in maze.
- Employ breadth-first search (BFS) algorithms on the Raspberry Pi to plan optimal solution path for navigating the ball through the maze.
- Integrate Arduino-controlled servos to physically manipulate ball in response to navigation com mands from the Raspberry Pi.
- Setup communication protocol between the Raspberry Pi and Arduino
Image Processing and Object Detection
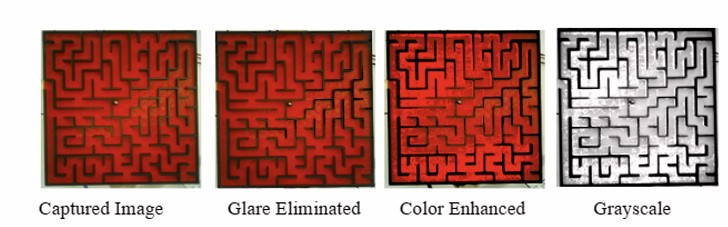
In order to accurately localize the position of the ball within the maze, a series of image processing steps are employed. First, the camera sensor’s exposure and gain settings are calibrated to ensure optimal image quality and contrast. Next, the captured image undergoes rotation and cropping to focus on the relevant area of interest within the maze. Following this, the image is converted to a suitable color space, to facilitate better detection of the ball. A masking technique is then applied to eliminate glare and enhance the colors, ensuring that the ball stands out against the background of the maze walls and path. This masking process isolates the ball while removing other colors from the image. Finally, the center and boundary of the ball are detected using the Hough Circles algorithm, allowing for precise localization within the maze. This detection process is repeated after every step taken by the ball, ensuring continuous tracking and accurate navigation within the maze environment.
Breadth First Search (BFS) Algorithm and incorporation
In the context of maze solving, BFS is used to find a solution path from a starting point to a destination point (or an exit). The maze will be represented as a graph, where each cell is a vertex, and the passages between cells are edges. By traversing the maze using BFS, we can efficiently find a solution path from the start cell to the end cell.
# Initialization
- Webegin by initializing a queue, which will store the vertices (cells) to be visited during the maze traversal.
- We also initialize a data structure (such as a matrix or list) to keep track of visited vertices to avoid revisiting the same cell.
- We enqueue the starting vertex (cell) into the queue and mark it as visited.
# BFS Traversal
- While the queue is not empty, we repeatedly dequeue a vertex from the front of the queue.
- For each dequeued vertex, we explore its neighboring vertices (cells) that have not been visited yet.
- For each unvisited neighboring vertex, we enqueue it into the queue and mark it as visited.
Rpi code
• Capture an image using the camera. • Process the image to detect ball and determine a solution path in the maze. • Send instructions to the Arduino based on the detected solution path.
# Arduino code • Receive instructions from the Raspberry Pi over serial communication (UART). • Control the servos to execute the specified rotations.
# Overall flow • The Raspberry Pi captures an image and processes it to determine ball position and a solution path in the maze. • Based on the relative position of ball with respect to the solution path, the Raspberry Pi sends instructions to the Arduino over serial communication. • The Arduino receives the instructions, controls the servos accordingly.